While installing or having an HVAC system in your house, it should be kept in mind that there are plenty of things that need to be known as HVAC is a big product. It includes various minor to major operations and sometimes a minor fault can cause major issues in it. Where all physical things may be examined and well known, some terms may become difficult for the HVAC owners to understand and visualize, one such term is superheat in HVAC.
If you have not heard about this before, you may ask, what is superheat in HVAC? Well, this is a process that should be known as it will make the troubleshooting process so easy while allowing you to resolve issues in your HVAC unit most efficiently and quickly.
What is superheat and why is it important
In simple words, superheat is a phenomenon when the gas exceeds a temperature way more than its boiling point. Almost all materials in the world are categorized as solid, liquid, or gas. Among all these three types, material only in gas form can reach the superheat point. Steam or vapor in the HVAC systems is also categorized as gas.
Superheat usually happens when a gas, vapor, or steam is heated to a temperature that is above the billing point of that material when it is in liquid form. For example, water at sea level starts to boil at 100°C in liquid form. You can experiment to see what superheat is by boiling water in a pot:
- Put some water in it and let it boil for a long time.
- Once it reaches 100°C, the temperature will stop at that place without increasing even a little bit.
- You can check the temperature using a thermometer.
- The temperature will not exceed 100°C until the water is in liquid form but once all the water has been evaporated, your thermometer will start to show a higher temperature.
- If the temperature is now 101°C, it can be said that water gas has been superheated by 1°C.
The process of superheat is more than important for any HVAC system because you don’t want a single drop of liquid to go inside the compressor after leaving the evaporator.
Superheat process in the evaporator allows the liquid refrigerant to evaporate completely even to the point that only steam or vapor can get inside the compressor.
This factor shows the importance of superheat because even a minor amount of liquid in the compressor can cause serious issues and getting a completely shut down or damaged compressor is one of them.
This is the reason that measuring superheat periodically is more than important as it allows you to troubleshoot the issue before it causes damages while ensuring your HVAC system runs efficiently for a longer time.
What does superheat tell you
Superheat gives you an exact idea of how much refrigerant is currently in the evaporator of an HVAC system.
If the superheat is high according to its normal range, it indicates minimum to almost no refrigerant in the evaporator. If the superheat value is low, it shows that there is more refrigerant in the evaporator.
If you are experiencing the latter one, it is a clear indication of issues that can surely lead to some major damages to the condenser in the long term if not taken care of immediately.
What is Superheat and Subcooling HVAC
As said earlier, superheat is the term that is used for the vapor or gas when they are heated above their boiling temperature. Superheat is an important factor in any HVAC system to keep it working perfectly for years without damaging the compressor or overall performance of the system.
Condensation or saturation is the process when the vapor of gas begins to turn back into liquid form. Subcooling is the lower temperature than the one at which a gas begins to turn into liquid. For example, if water gas is condensed at 100°C, the temperature lower from this range will be known as the subcooling point.
Superheat and subcooling formula
The formula to calculate both superheat and subcooling is more than easy as all you need to do is just subtract the current temperature from the boiling or condensation temperature of the water gas.
If you are calculating superheat, you will need to subtract the current temperature from the boiling temperature which will be as:
- Superheat = Current Temperature – Boiling Temperature
- Superheat = 102°C – 100°C
- Superheat = 2°C
If you need to derive subcooling in HVAC, you can simply subtract condensation temperature from current temperature as:
- Subcooling = Condensation Temperature – Current Temperature
- Subcooling = 100°C – 90°C
- Subcooling = 10°C
Do keep this fact in mind that boiling as well as condensation temperature of the water is the same at 100°C or 212°F.
How to check superheat HVAC
- Sart by measuring the suction pressure and its temperature. A suction side service valve is the most appropriate place to use a thermostat for measuring temperature.
- Temperature probes or thermostats should always be insulated to protect them from external temperature disturbances
- If you have measured gauge pressure, convert it into condensation temperature also known as saturation temperature.
- Subtract the condensation temperature from the temperature measured at the suction line.
- The value after subtraction will be the exact superheat.
How to measure subcooling
- Start by measuring the pressure of air or gas on the high side of the receiver or pressure gauge of the HVAC system.
- You need to convert the pressure into temperature which can easily be done using a temperature/pressure comparator device.
- Now by using a thermostat or temperature probe, take the current temperature of the liquid that is just leaving the condenser.
- Now it’s time to subtract the current temperature from the one that was converted from the gauge pressure.
- The resultant value is the subcooling of your HVAC system.
How to use superheat and subcooling
There is only one thing that requires measuring superheat and subcooling in any HVAC system and that is to maintain both of these things at a point that is perfect for the system. You can use the measured values of these processes in getting your system repaired or modified accordingly.
For example, if superheat is too low, you can use this value to make changes so that the evaporator can produce more heat and if subcooling is too high, you can increase temperature near the compressor or evaporator to protect it from condensation.
How to calculate superheat r22
- While calculating the superheat R-22 system, simply put a thermostat at the suction line and record the pressure.
- Make sure that you don’t use an infrared thermostat or one without insulation as it may alter values.
- Use a pressure/temperature chart or comparator to convert taken suction line pressure into temperature.
- Subtract current and above-derived temperature and you will get the superheat value.
- Subcooling can also be measured using the same technique however the formula is a bit different as it is described above.
How to calculate superheat 404a
- At the condenser coil, attach the suction also known as low side refrigerant gauge to the suction line service port of the HVAC system.
- Now put a clamp on the digital temperature recording or sensing probe. It should be put too closely on the condenser coil.
- Take note of all the pressure and temperature values from the suction high or low side gauge.
- Once you have gathered all these values, simply put them into the superheat calculation formulas and you will get the exact superheat in your HVAC system.
What is the target superheat in HVAC
An appropriate range of superheat temperature may vary in different HVAC systems but not to a great margin. Most of the experts and manufacturers claim that a superheat temperature of 10°F near the evaporator is just perfect for the system.
This range should be as much as 20°F to 25°F just before the air tries to enter the comparator. Although these are considered the best suitable superheat temperatures for any HVAC system, the minimum range is from 4°C to 6°C.
If the superheat in your HVAC is even less than the minimum range, it is best to contact a professional and get your systems analyzed property.
What happens when you superheat air
When air is superheated inside the HVAC systems, even the nanoparticles of water or moisture are turned completely into gas or vapor.
Some people confuse between boiling point and superheat as they think that water will be converted into gas once it reaches the 100 degrees Celsius mark but the fact is that this point is just the beginning mark.
Water requires extra heat to reach the superheat process. Superheating air will protect the compressor from moisture at one place and increase its lifespan, working, and performance on the other.
Having good superheat in HVAC also mitigates the energy wastages that eventually decrease your utility bills as well.
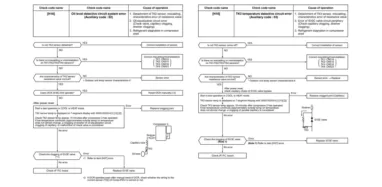
Superheat and subcooling troubleshooting
Troubleshooting superheat or subcooling is an easy job as all you need is to measure two temperatures and airflow to get exact values.
Where high superheat may not cause any issues, low superheat can cause serious damages and you need to troubleshoot superheat instead of issues after the damage has been done.
Subcooling troubleshooting is also very important because condensed water can still get inside the condenser and do the same that low superheat can do.
Troubleshooting HVAC systems using superheat and subcooling
Superheat and subcooling can easily be troubleshot with a thermometer as you need to measure temperatures.
The temperatures should first be measured near the evaporated to find the initial temperature and then measure it from the compressor end as the vapor reaches that point.
Although you can simply use a thermometer for measuring procedures, insulating it is usually recommended by the experts so that no external disturbance can cause any ups or downs in the measured values.
How to check superheat and subcooling in heat mode
You can follow the same procedure as mentioned above during the heat mode as well. The only difference is that the values may vary but not to a great extent.
Make sure you measure temperature at least two to three times and then take an average before putting them into the calculation formula of superheating and subcooling.
What causes low superheat in HVAC
There are various causes of this problem while some of the most prominent are mentioned below:
- Insufficient heat is reaching or getting to the evaporator.
- Blocked, clogged, plugged, or dirty evaporator coil.
- A buildup of dust and dirt on the blower wheel.
- Restricted or undersized ductwork.
- Slipping of the belt.
- Dirty or clogged filter.
How to fix low superheat in HVAC
- Start by turning the screw clockwise as it will increase the superheat in the HVAC system.
- Increase the heat load so that the refrigerant in the system can be heated to a higher level which will fix low superheat to a greater extent.
- Recover the amount of refrigerant from the system as it will also increase suction superheat.
What causes high superheat in HVAC
Superheat can be caused due to various reasons while some can easily be controlled while others need proper professional help. Some of the most prominent causes that can lead to high superheat in HVAC include:
- Undercharged system.
- Restriction of refrigerant.
- Excessive evaporator heat loads in the system.
- Blockages in filter drier.
- Too much moisture in the system.
- Metering devices could be a cause if it is underfeeding to the system.
- High superheat can also occur if the metering device is damaged, broken, or not adjusted properly.
What to do if the superheat is too high
If the superheat in your HVAC system is high way more than the normal range, you can easily get it down by adding more refrigerant to bring it back to normal range.
Either increase the load or call a professional to deal with this problem as too much superheat can also cause damages to the compressor.
An increase in superheat will grow the heat of compression inside the HVAC system which can become a cause of the increase in temperature at the discharge valves. The constant process of high superheat will make the oil lose its lubricant which can eventually lead to premature wear or damages of cylinder piston rings and cylinder.
More resources: